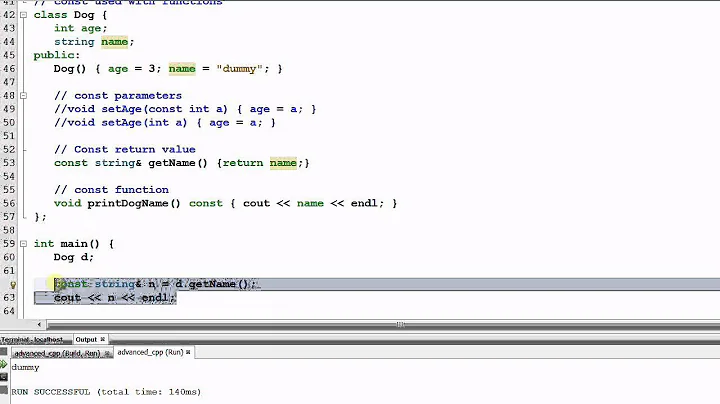
Cannot call a method of const reference parameter in C++
11,127
You can't call non-const member functions via const references. You can fix this by making the member function const:
void method() const {};
^^^^^
This indicates that calling the member does not mutate the object it is called on*
* Conceptually. In practice it can mutate members marked mutable
Related videos on Youtube
Author by
Mr Cold
Updated on June 05, 2022Comments
-
 Mr Cold almost 2 years
Mr Cold almost 2 yearsclass A { public: A(){}; ~A(){}; void method(){}; }; void call(const A &a) { a.method(); // I cannot call this method here if I use "const" but I can call it if not using "const" } int main() { A a; call(a); return 0; }In this case, the error is: "
passing const A as this argument of void A::method() discards qualifiers [-fpermissive]|"In function
call, if I useconst, I get the error, but if I get rid of it, it works.Can anyone explain it for me?
-
 Lightness Races in Orbit about 9 yearsWhat do you think the
Lightness Races in Orbit about 9 yearsWhat do you think theconstdoes? -
 Lightness Races in Orbit about 9 years@MrCold: The only reason that code doesn't work is because you have a bug in the
Lightness Races in Orbit about 9 years@MrCold: The only reason that code doesn't work is because you have a bug in theoperator[]that you randomly added and that has nothing to do with this question. Try to change just one thing at a time when you are trying to solve problems. If you'd only added theconsttomethod(), you'd have seen that it works fine.
-
-
 Mr Cold about 9 yearsThank you for your answer but this as I see this rule does not work with overloading operator [] as follow: pastebin.com/1mKek7pM Can you explain more?
Mr Cold about 9 yearsThank you for your answer but this as I see this rule does not work with overloading operator [] as follow: pastebin.com/1mKek7pM Can you explain more? -
juanchopanza about 9 years@MrCold What do you mean "this rule doesn't work"? Do you mean it doesn't compile? That is because you are returning a non-const reference to a data member via a const reference to the object.
-
juanchopanza about 9 years@MrCold In other words, the const overload should return a
constreference (or a value):const int& operator [] (int i) const {return num;}. You can also add a non-const overload for when you want to be able to modify the data member:int& operator [] (int i) {return num;} -
 Mr Cold about 9 yearsOh, i got it. Thank you very much for your explanation :)
Mr Cold about 9 yearsOh, i got it. Thank you very much for your explanation :)