How do I restart the SSH service?
Solution 1
15.04 and newer:
Use this command:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
To restart the SSH server/daemon.
Going forward with systemd starting with Ubuntu 15.04, you now use this syntax to stop, start, or restart services:
sudo systemctl <action> <service-name>
Solution 2
Command for restart ssh service is:
sudo service ssh restart
Solution 3
Pre 15.04:
It should be as simple as (tested on a fresh install with openssh-server)
sudo stop ssh
sudo start ssh
As it leverages upstart, this is The Best Way™ to do it, rather than using /etc/init.d/ssh, service, or invoking sshd directly. Make sure to run both commands; if you get an error on stop ssh, start ssh anyway and see what it says—the service could already be stopped.
(I would recommend stop/start over restart, unless you are trying to restart a system remotely. If ssh is already stopped, restart will not start it.)
If those commands don't work, you are probably either experiencing a bug or have tinkered too far with your system, in which case you at least know what the problem isn't.
Solution 4
Since Ubuntu 15.04, Canonical no longer ships upstart by default.
Thus, the commands start, stop and restart are no longer available.
The correct method for restarting the SSH service (or any other service) now is one of the two following commands:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
sudo service ssh restart
Solution 5
On Ubuntu Desktop:
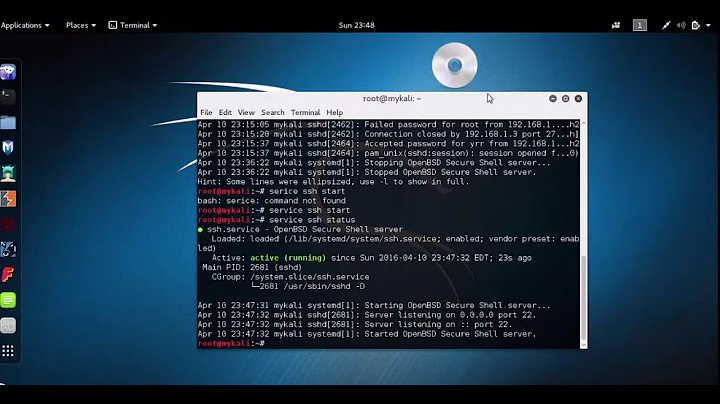
First check the status of the service:
sudo service ssh status
should show: - Active: active (running) If it's running there's no need to restart it.
If you still want to restart it, Ubuntu calls the service ssh, not sshd.
service ssh restart
But if its not Ubuntu Desktop, using CLI:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
sudo service ssh restart
The service is also controlled by upstart, and not sysvinit. So you'll find it at /etc/init/ssh.conf instead of /etc/init.d/ssh.
If you want to change some settings (e.g., the listening port, and root login permission) by editing the configuration file via command:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
On Ubuntu desktop, you may use gedit instead of nano:
Finally apply the changes by restarting or reloading SSH:
sudo service ssh restart
If above still doesn't work then, type this:
sudo service ssh stop
sudo service ssh start
If all above fails, try restarting your ubuntu system:
sudo reboot -f
Related videos on Youtube
mia_tech
Updated on September 18, 2022Comments
-
mia_tech over 1 year
How do I stop/start ssh? I've tried
/etc/init.d/ssh restart sudo service ssh restart sudo restart sshI get errors every time.
-
 Scott Stensland over 7 yearsIMPORTANT - do not install openssh-server on your local machine (laptop/desktop) unless you wish to permit incoming connections from other remote machines ... you do NOT need this package to ssh to other machines since ubuntu comes with the Client half of this Server
Scott Stensland over 7 yearsIMPORTANT - do not install openssh-server on your local machine (laptop/desktop) unless you wish to permit incoming connections from other remote machines ... you do NOT need this package to ssh to other machines since ubuntu comes with the Client half of this Server
-
-
 Alex Punnen about 7 years
Alex Punnen about 7 years -
 pa4080 over 6 years
pa4080 over 6 years -
 Serge Stroobandt about 3 yearsAfterwards, check the status of the SSH daemon using
Serge Stroobandt about 3 yearsAfterwards, check the status of the SSH daemon usingsudo systemctl status ssh -
openCivilisation almost 3 yearsOn ubuntu 18 I get
Failed to restart ssh.service: Unit ssh.service not found. -
Gringo Suave over 2 years
alias sc='sudo systemctl'quicker and matches a similar util on Windows. ;-)