Is HTML Turing Complete?
It seems clear to me that states and transitions can be represented in HTML with pages and hyperlinks, respectively. With this, one can implement deterministic finite automata where clicking links transitions between states. For example, I implemented a few simple DFA which are accessible here.
DFA are much simpler that the Turing Machine though. To implement something closer to a TM, an additional mechanism involving reading and writing to memory would be necessary, besides the basic states/transitions functionality. However, HTML does not seem to have this kind of feature. So I would say HTML is not Turing-complete, but is able to simulate DFA.
Edit: I was reminded of the video On The Turing Completeness of PowerPoint when writing this answer.
Edit: complementing this answer with the DFA definition and clarification.
Definition
From https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deterministic_finite_automaton#Formal_definition
In the theory of computation, a branch of theoretical computer science, a deterministic finite automaton (DFA)—also known as deterministic finite acceptor (DFA), deterministic finite-state machine (DFSM), or deterministic finite-state automaton (DFSA)—is a finite-state machine that accepts or rejects a given string of symbols, by running through a state sequence uniquely determined by the string.
A deterministic finite automaton M is a 5-tuple, (Q, Σ, δ, q0, F), consisting of
- a finite set of states Q
- a finite set of input symbols called the alphabet Σ
- a transition function δ : Q × Σ → Q
- an initial or start state q0
- a set of accept states F
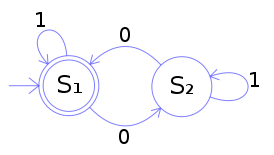
The following example is of a DFA M, with a binary alphabet, which requires that the input contains an even number of 0s.
M = (Q, Σ, δ, q0, F) where
- Q = {S1, S2}
- Σ = {0, 1}
- q0 = S1
- F = {S1} and
- δ is defined by the following state transition table:
0 0 s1 s2 s1 s2 s1 s2 State diagram for M:
The state S1 represents that there has been an even number of 0s in the input so far, while S2 signifies an odd number. A 1 in the input does not change the state of the automaton. When the input ends, the state will show whether the input contained an even number of 0s or not. If the input did contain an even number of 0s, M will finish in state S1, an accepting state, so the input string will be accepted.
HTML implementation
The DFA M exemplified above plus a few of the most basic DFA were implemented in Markdown and converted/hosted as HTML pages by Github, accessible here.
Following the definition of M, its HTML implementation is detailed as follows.
- The set of states Q contains the pages
s1.htmlands2.html, and also the acceptance pageacc.htmland the rejection pagerej.html. These two additional states are a "user-friendly" way to communicate the acceptance of a word and don't affect the semantics of the DFA. - The set of symbols Σ is defined as the symbols 0 and 1. The empty string symbol ε was also included to denote the end of the input, leading to either
acc.htmlorrej.htmlstate. - The initial state q0 is
s1.html. - The set of accept states is {
acc.html}. - The set of transitions is defined by hyperlinks such that page
s1.htmlcontains a link with text "0" leading tos2.html, a link with text "1" leading tos1.html, and a link with text "ε" leading toacc.html. Each page is analogous according to the following transition table. Obs:acc.htmlandrej.htmldon't contain links.
| 0 | 1 | ε | |
|---|---|---|---|
| s1.html | s2.html | s1.html | acc.html |
| s2.html | s1.html | s2.html | rej.html |
Questions
- In what ways are those HTML pages "machines"? Don't these machines include the browser and the person who clicks the links? In what way does a link perform computation?
DFA is an abstract machine, i.e. a mathematical object. By the definition shown above, it is a tuple that defines transition rules between states according to a set of symbols. A real-world implementation of these rules (i.e. who keeps track of the current state, looks up the transition table and updates the current state accordingly) is then outside the scope of the definition. And for that matter, a Turing machine is a similar tuple with a few more elements to it.
As described above, the HTML implementation represents the DFA M in full: every state and every transition is represented by a page and a link respectively. Browsers, clicks and CPUs are then irrelevant in the context of the DFA.
In other words, as written by @Not_Here in the comments:
Rules don't innately implement themselves, they're just rules an implementation should follow. Consider it this way: Turing machines aren't actual machines, Turing didn't build machines. They're purely mathematical objects, they're tuples of sets (state, symbols) and a transition function between states. Turing machines are purely mathematical objects, they're sets of instructions for how to implement a computation, and so is this example in HTML.
The Wikipedia article on abstract machines:
An abstract machine, also called an abstract computer, is a theoretical computer used for defining a model of computation. Abstraction of computing processes is used in both the computer science and computer engineering disciplines and usually assumes a discrete time paradigm.
In the theory of computation, abstract machines are often used in thought experiments regarding computability or to analyze the complexity of algorithms (see computational complexity theory). A typical abstract machine consists of a definition in terms of input, output, and the set of allowable operations used to turn the former into the latter. The best-known example is the Turing machine.
Comments
-
 Luke 11 months
Luke 11 monthsAfter reading this question Is CSS Turing complete? -- which received a few thoughtful, succinct answers -- it made me wonder: Is HTML Turing Complete?
Although the short answer is a definitive Yes or No, please also provide a short description or counter-example to prove whether HTML is or is not Turing Complete (obviously it cannot be both). Information on other versions of HTML may be interesting, but the correct answer should answer this for HTML5.
-
 Anthony Yershov almost 3 years"In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules is said to be Turing-complete or computationally universal if it can be used to simulate any Turing machine. This means that this system is able to recognize or decide other data-manipulation rule sets." - wiki definition. Your system would also include a human who would do the clicking, so it's not pure HTML. I'm pretty sure when people say that javascript is turing complete, they mean the engine and not the syntax.
Anthony Yershov almost 3 years"In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules is said to be Turing-complete or computationally universal if it can be used to simulate any Turing machine. This means that this system is able to recognize or decide other data-manipulation rule sets." - wiki definition. Your system would also include a human who would do the clicking, so it's not pure HTML. I'm pretty sure when people say that javascript is turing complete, they mean the engine and not the syntax. -
 bwdm almost 3 years@Anthony Yershov Computability theory is more abstract than that. You don't need an interpreter or even a CPU to determine the computational power of such a rule (e.g. a formal grammar). This kind of analysis is all about the syntax, not the implementation of the mechanism for transitioning between states. So I would say it's pure HTML as much as any formal grammar is "pure".
bwdm almost 3 years@Anthony Yershov Computability theory is more abstract than that. You don't need an interpreter or even a CPU to determine the computational power of such a rule (e.g. a formal grammar). This kind of analysis is all about the syntax, not the implementation of the mechanism for transitioning between states. So I would say it's pure HTML as much as any formal grammar is "pure". -
 Anthony Yershov almost 3 yearsA link doesn't perform any logical calculation on its own, so I would argue that it couldn't be used to represent state transfer.
Anthony Yershov almost 3 yearsA link doesn't perform any logical calculation on its own, so I would argue that it couldn't be used to represent state transfer. -
 bwdm almost 3 yearsThe hyperlinks not only represent states transitions, they also work. You can test it yourself.
bwdm almost 3 yearsThe hyperlinks not only represent states transitions, they also work. You can test it yourself. -
 sfdcfox over 2 yearsIt seems to me that the DFA would be the browser, not HTML itself. The state representation is the URL for each page, not within its HTML. The HTML itself isn't even aware of its own state, but the browser is.
sfdcfox over 2 yearsIt seems to me that the DFA would be the browser, not HTML itself. The state representation is the URL for each page, not within its HTML. The HTML itself isn't even aware of its own state, but the browser is. -
 bwdm over 2 years@sfdcfox Again, it's more abstract than that. This simple tuple is a DFA, and that's what I implemented with the HTML pages above. The browser is just a mechanism to simulate it, and it's not part of the DFA. So the browser just happens to act it out, thus behaving like a DFA because it's following one.
bwdm over 2 years@sfdcfox Again, it's more abstract than that. This simple tuple is a DFA, and that's what I implemented with the HTML pages above. The browser is just a mechanism to simulate it, and it's not part of the DFA. So the browser just happens to act it out, thus behaving like a DFA because it's following one. -
 sfdcfox over 2 yearsI did read that to make sure I had the right idea. It still seems to me that each HTML page is a node, or state, within a collection of files laid out in a DFA, just like you can with, say, a file system. In the example you linked, the 0/1 would be the href/link, the S1/S2 would be the pages. They are nodes within a larger system laid out as a DFA, but are not inherently a DFA in and of themselves, no more than any single cell in your body is "you." Anyways, was just my two cents. You've given me something to think about. Thanks!
sfdcfox over 2 yearsI did read that to make sure I had the right idea. It still seems to me that each HTML page is a node, or state, within a collection of files laid out in a DFA, just like you can with, say, a file system. In the example you linked, the 0/1 would be the href/link, the S1/S2 would be the pages. They are nodes within a larger system laid out as a DFA, but are not inherently a DFA in and of themselves, no more than any single cell in your body is "you." Anyways, was just my two cents. You've given me something to think about. Thanks! -
 Admin over 2 years@AnthonyYershov In your quote "a system of data-manipulation rules" goes against what you are trying to argue. Rules don't innately implement themselves, they're just rules an implementation should follow. Consider it this way: Turing machines aren't actual machines, Turing didn't build machines. They're purely mathematical objects, they're tuples of sets (state, symbols) and a transition function between states. Turing machines are purely mathematical objects, they're sets of instructions for how to implement a computation, and so is this example in HTML.
Admin over 2 years@AnthonyYershov In your quote "a system of data-manipulation rules" goes against what you are trying to argue. Rules don't innately implement themselves, they're just rules an implementation should follow. Consider it this way: Turing machines aren't actual machines, Turing didn't build machines. They're purely mathematical objects, they're tuples of sets (state, symbols) and a transition function between states. Turing machines are purely mathematical objects, they're sets of instructions for how to implement a computation, and so is this example in HTML.