Large AWS Regional Data Transfer cost; ELB to blame?
Your suspicion is correct.
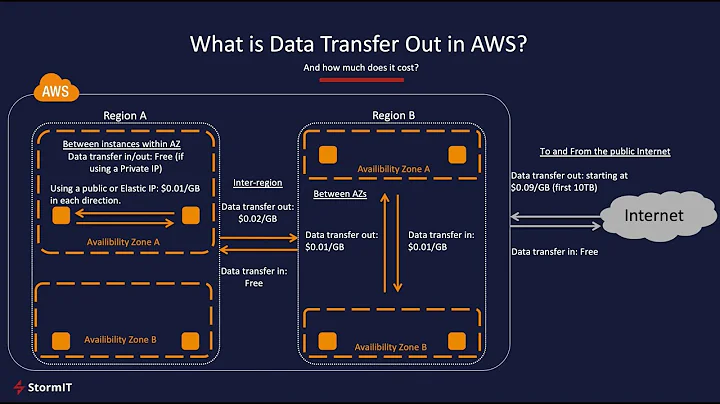
If you communicate between instances using public or elastic IP address even in the same region you pay regional data transfer rates (0.01$ per GB in/out):
Public and Elastic IP and Elastic Load Balancing Data Transfer
$0.01 per GB in/out – If you choose to communicate using your Public or Elastic IP address or Elastic Load Balancer inside of the Amazon EC2 network, you’ll pay Regional Data Transfer rates even if the instances are in the same Availability Zone. For data transfer within the same Availability Zone, you can easily avoid this charge (and get better network performance) by using your private IP whenever possible.
As stated in the EC2 FAQ: If I transfer data between Availability Zones using public IP addresses, will I be charged twice for Regional Data Transfer (once because it’s across zones, and a second time because I’m using public IP addresses)?.
The solution is to always "use the internal address when you are communicating between Amazon EC2 instances [which] ensures that your network traffic follows the highest bandwidth, lowest cost, and lowest latency path through our network".
Related videos on Youtube
Graham
Updated on September 18, 2022Comments
-
Graham over 1 year
Recently an AWS account I'm handling has seen a large increase in the Regional Data Transfer cost. Inspecting the usage / bill details reveals this is down to an increase in "ELB data" being processed and "Regional Data Transfer".
All the instances are in the same availability zone, so the issue must be the load balancers. There are 2 ELBs for internet-facing traffic and 2 ELBs for internal traffic, however looking at the console I can see all 4 are Classic ELBs talking to instances inside EC2-Classic rather than a VPC.
Because of this, the 2 "internal" ELBs are being referenced by a DNS name in the form
ELB-Name-loadbalancer-xxxxxxx.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com, rather than theInternal-loadbalancer-xxxxxxx.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.comcreated with internal ELBs.Presumably these DNS records resolve to public IPs, and would therefore incur the data-transfer cost? If this is the case, variations in the TTL could theoretically cause the cost variations I'm seeing.
Can anyone confirm if this is correct or if I'm mistaken (and if so, what else I could do to help trace the problem)?
EDIT: Here's a chart of what I'm seeing:
While data in/out is flat, ELB data & Regional transfer are increasing like crazy. Interestingly ELB data is roughly half of the regional data transfer, so I think that would correlate with my guess that the ELB traffic is getting charged in/out. Unfortunately I have no idea what's causing the actual increase in the ELB data itself.
-
hookenz over 7 years
-
hookenz over 7 yearsAccording to that link, data transfer costs increase with public or elastic IP.
-
hookenz over 7 yearsWas anything change at the beginning of Sept?
-
Graham over 7 years@Matt - at most I added / removed some instances attached to the web-facing ELB. No increase in traffic or changes to architecture
-
-
Graham over 7 yearsThanks for the links. OK, so I'll have to recreate some instances inside a VPC and attach them to new internal ELBs. I just need to figure out what's causing the actual increase in ELB data...!
-
 Gaia over 7 yearsTry the AWS forum for specific help on how to properly route. Include screenshots of the config of the involved machines. Or find a consulting partner that can assist you: aws.amazon.com/partners/find
Gaia over 7 yearsTry the AWS forum for specific help on how to properly route. Include screenshots of the config of the involved machines. Or find a consulting partner that can assist you: aws.amazon.com/partners/find