What is the purpose of the Java Constant Pool?
Solution 1
I think understanding how the frame is constructed using a diagram would help.

The frame is where the operands (operation instructions) reside and that is where the dynamic linking occurs. It is a shorthand way, so to speak, using the constant pool to keep track of the class and it's members.
Each frame contains a reference to the runtime constant pool. The reference points to the constant pool for the class of the method being executed for that frame. This reference helps to support dynamic linking.
C/C++ code is typically compiled to an object file then multiple object files are linked together to product a usable artifact such as an executable or dll. During the linking phase symbolic references in each object file are replaced with an actual memory address relative to the final executable. In Java this linking phase is done dynamically at runtime.
When a Java file is compiled, all references to variables and methods are stored in the class's constant pool as a symbolic reference. A symbolic reference is a logical reference not a reference that actually points to a physical memory location.
Here is a link to James Blooms JVM Internals for more details.
Solution 2
Constant pool is a part of .class file (and its in-memory representation) that contains constants needed to run the code of that class.
These constants include literals specified by the programmer and symbolic references generated by compiler. Symbolic references are basically names of classes, methods and fields referenced from the code. These references are used by the JVM to link your code to other classes it depends on.
For example, the following code
System.out.println("Hello, world!");
produces the following bytecode (javap output)
0: getstatic #2; //Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
3: ldc #3; //String Hello, world!
5: invokevirtual #4; //Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#n here are references to the constant pool. #2 is a symbolic reference to System.out field, #3 is a Hello, world! string and #4 is a symbolic reference to PrintStream.println(String) method.
As you can see, symbolic references are not just names - for example, symbolic reference to the method also contains information about its parameters (Ljava/lang/String;) and return type (V means void).
You can inspect constant pool of a class by running javap -verbose for that class.
Solution 3
What is the Constant Pool's purpose, in simple English?
The CP is a memory area very unique constant values are stored to reduce redundancy:
System.err.println("Hello");
System.out.println("Hello");
In the CP there is only one String object "Hello" and the compiler substitutes in both lines to the same reference. Your .class file only contains one Hello string. (The same for other types).
Is CP located in .Class file for each type?
Yes, Look here: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_class_file
Solution 4
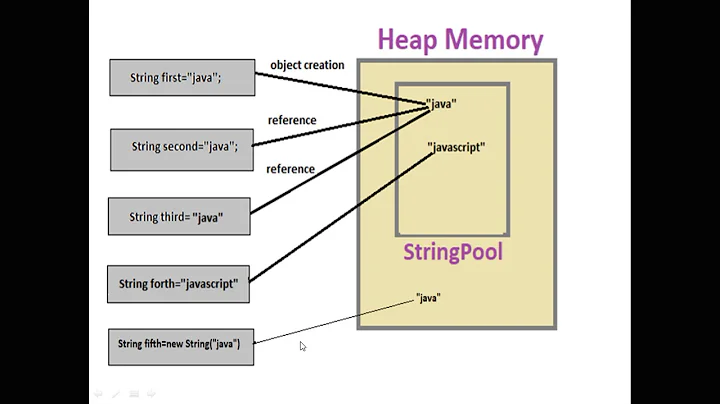
Let give Example First to understand what String constant pool mean
public class StringConstantPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "prasad";
String s2 = "prasad";
System.out.println(s.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s == s2);
}
}
the output will be
true
true
what happen here step by step
1- The class is loaded when JVM is invoked.
2- JVM will look for all the string literals in the program.
3- First, it finds the variable s which refers to the literal “prasad” and it will be created in the memory
4- A reference for the literal “prasad” will be placed in the string constant pool memory.
5- Then it finds another variable s2 which is referring to the same string literal “prasad“.
Now that JVM has already found a string literal “prasad“, both the variables s and s2 wil refer to the same object i.e. “prasad“.

I hope this be helpful
read more http://www.journaldev.com/797/what-is-java-string-pool
Related videos on Youtube
Comments
-
Bober02 almost 4 years
I am currently trying to dig deeper into the specification of the Java Virtual Machine. I have been reading Inside the JVM book online and there is one confusing abstraction I can't seem to grasp: Constant Pool. here is the excerpt from the book:
For each type it loads, a Java virtual machine must store a constant pool. A constant pool is an ordered set of constants used by the type, including literals (string, integer, and floating point constants) and symbolic references to types, fields, and methods. Entries in the constant pool are referenced by index, much like the elements of an array. Because it holds symbolic references to all types, fields, and methods used by a type, the constant pool plays a central role in the dynamic linking of Java programs
I have several questions about the above and CP in general:
- Is CP located in
.classfile for each type? - What does the author mean by "symbolic reference"?
- What is the Constant Pool's purpose, in simple English?
- Is CP located in
-
Bober02 about 12 yearsWould you expand a bit more on the symbolic links perhaps? I think these are most important part of CP
-
hitesh israni about 12 years@axtavt- wow! nice explanation. looks like a little typo near "#3 is a symbolic reference to PrintStream.." should'nt it be #4
-
JackWM about 12 yearsBut what does "L" mean in "Ljava/lang/String;" ?
-
axtavt about 12 years@JackWM: See
Class.getName(). -
Mercenary over 10 yearsThere is basically just one run-time constant pool created by JVM right? Or is there a separate constant pool for every .class files?
-
Mercenary over 10 yearsAlso, is string intern pool a part of run-time constant pool?
-
Matthias Braun over 10 yearsThere is a constant pool inside every class file. It is created by the compiler. The JVM resolves the references of the CP during runtime. The string intern pool is an area inside the VM.
-
 Keenle over 9 yearsThere is not such thing as 'String constant pool'. There is 'Constant pool' that exist in each class file and there is 'String pool' of interned strings that exist for JVM.
Keenle over 9 yearsThere is not such thing as 'String constant pool'. There is 'Constant pool' that exist in each class file and there is 'String pool' of interned strings that exist for JVM. -
Mina Fawzy over 9 yearsyea , here I meant String pool , Thank you for comment
-
 Koray Tugay about 9 years"When a Java class is compiled..." ? Isn't a .class file already a compiled Java code?
Koray Tugay about 9 years"When a Java class is compiled..." ? Isn't a .class file already a compiled Java code? -
 Koray Tugay about 9 yearsThank you for the answer. This is the second time I see this answer.
Koray Tugay about 9 yearsThank you for the answer. This is the second time I see this answer. -
 James Drinkard about 9 yearsYes, a .java file becomes a .class file when compiled.
James Drinkard about 9 yearsYes, a .java file becomes a .class file when compiled. -
overexchange almost 9 yearsI think the author of this answer is talking about
cp_info constant_pool[constant_pool_count-1];inClassFile {..} -
 James Drinkard over 8 yearsAll his links are broken. I'll check back later to see if he reposts it again.
James Drinkard over 8 yearsAll his links are broken. I'll check back later to see if he reposts it again. -
 James Drinkard almost 8 yearsThe link is fixed again.
James Drinkard almost 8 yearsThe link is fixed again. -
 Yamcha over 6 years"operands (operation instructions) ...". Operands aren't the same as operation instructions as suggested. right?
Yamcha over 6 years"operands (operation instructions) ...". Operands aren't the same as operation instructions as suggested. right? -
 jones j alapat almost 3 yearsFew updates in the diagram: As of Java 8 HotSpot VM, permanent generation is replaced with Metaspace. Method Area would be represented as Metaspace(HotSpot VM) and run Time Constant pool memory would still be allocated from Method Area as before. The other diff is from Java 7, Intern String Pool would be part of Heap.
jones j alapat almost 3 yearsFew updates in the diagram: As of Java 8 HotSpot VM, permanent generation is replaced with Metaspace. Method Area would be represented as Metaspace(HotSpot VM) and run Time Constant pool memory would still be allocated from Method Area as before. The other diff is from Java 7, Intern String Pool would be part of Heap. -
 James Drinkard almost 3 yearsI'm always reminding people to refer to their JAVA version in Q&A as it makes for a better reference. I didn't do that here.
James Drinkard almost 3 yearsI'm always reminding people to refer to their JAVA version in Q&A as it makes for a better reference. I didn't do that here.