Add new server to Server Manager, get Kerberos error 0x80090322
Solution 1
Ok, I finally figured it out. I took another good look at the event log of the remote server. It contained an error with the following error text:
The Kerberos client received a KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED error from the server srv003. The target name used was HTTP/srv003.rwwilden01.local. This indicates that the target server failed to decrypt the ticket provided by the client. This can occur when the target server principal name (SPN) is registered on an account other than the account the target service is using. Ensure that the target SPN is only registered on the account used by the server. This error can also happen if the target service account password is different than what is configured on the Kerberos Key Distribution Center for that target service. Ensure that the service on the server and the KDC are both configured to use the same password. If the server name is not fully qualified, and the target domain (RWWILDEN01.LOCAL) is different from the client domain (RWWILDEN01.LOCAL), check if there are identically named server accounts in these two domains, or use the fully-qualified name to identify the server.
It appeared I had added a managed service account a week earlier with SPN HTTP/srv003.rwwilden.local. I'm not sure why Server Manager attempts this target name first but apparently this doesn't work. Makes sense since this SPN has little to do with the actual server.
After I removed the service account, everything started working as I intended.
Solution 2
I couldn't add a comment (New job, new account, no points)to the post I wanted to so I'm replying. The reason why using an IP helps/solves the problem is because when an IP is used Kerberos is not used. Kerb is only attempted when a FQDN is used (or a NBT name but that's only because it appends the domain name making it fqdn anyways). Generally speaking most Kerberos errors are because of either naming OR the SPN not being set or set correctly for the service you require. Cnames don't work btw unless you turn off strict name checking and even then will not work under some circumstances so I suggest you stay away from them at least while diagnosing. But honestly...the BEST approach to figure this kind of stuff out (because Windows logs and Kerb aren't that helpful) is to use Wireshark. you will see the negotiation and you will see why it fails, what its trying, etc. Additionally if you enable "analytic and debug" logs in Event viewer you will get additional debug logs for Kerb that you can enable that are a bit more helpful. Still...Wireshark is always your friend imho!
Solution 3
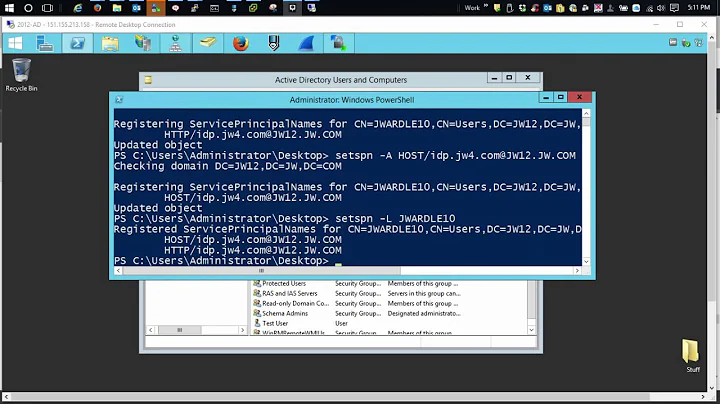
I had this problem not long ago, I got pointed towards the culprit by using the "setspn" tool. I got a better understanding of SPNs by reading this article : http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;929650
Solution 4
Had same error and tried many different solutions. The one that helped was to use explicit IPv4 address instead of domain name.
Solution 5
In my case, I had an HTTP/ SPN registered to an object that was owned by NOT the server. However, I couldn't find what owned it because the SETSPN.exe tool doesn't show you what container (or object) owns the SPN. I used the following PowerShell script to find the SPN's owner. After I deleted the SPN and recreated it with the server as the owner (using the SETSPN.exe tool), I waited 30 minutes for all the DCs to synchronize and then it worked.
# Source / credit:
# https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/18996.active-directory-powershell-script-to-list-all-spns-used.aspx
Clear-Host
$Search = New-Object DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher([ADSI]"")
$Search.Filter="(servicePrincipalName=*)"
## You can use this to filter for OU's:
## $Results = $Search.FindAll() | ?{ $_.Path -like '*OU=whatever,DC=whatever,DC=whatever*' }
$Results=$Search.FindAll()
foreach($Result in $Results ) {
$UserEntry=$Result.GetDirectoryEntry()
Write-Host "Object Name = " $UserEntry.name -BackgroundColor "yellow" -ForegroundColor "black"
Write-Host "DN = " $UserEntry.distinguishedName
Write-Host "Object Cat. = " $UserEntry.objectCategory
Write-Host "servicePrincipalNames"
$i=1
foreach($SPN in $UserEntry.servicePrincipalName ) {
Write-host "SPN(" $i ") = " $SPN
$i++
}
Write-Host ""
}
Related videos on Youtube
larsbeck
Updated on September 18, 2022Comments
-
larsbeck over 1 year
I'm setting up a Windows lab environment. It has a Win2012R2 domain controller (srv001) and I'd like to add another Win2012R2 server to the domain (srv003). Actually, all goes well. I gave the new server a static IP address in the same subnet as the DC, pointed it to the right DNS server and added the server to the domain.
However, when I add the new server to Server Manager, I get a Kerberos error: 0x80090322. I has quite a long error message that I'll post below. I did some testing and found out that I'm actually able to setup a remote Powershell session to the server using Kerberos authentication:
$s = New-PSSession -ComputerName srv003 -Authentication Kerberos $s | Enter-PSSessionNo problems here. I ran
Enable-PSRemotingon the remote server, no problems there as well.Why doesn't Server Manager like my new server? Especially since it's possible to set up a remote Powershell using the same protocol Server Manager is complaining about.
The error message that belongs to error code 0x80090322:
Configuration refresh failed with the following error: The metadata failed to be retrieved from the server, due to the following error: WinRM cannot process the request. The following error with errorcode 0x80090322 occurred while using Kerberos authentication: An unknown security error occurred. Possible causes are:
- The user name or password specified are invalid.
- Kerberos is used when no authentication method and no user name are specified.
- Kerberos accepts domain user names, but not local user names.
- The Service Principal Name (SPN) for the remote computer name and port does not exist.
- The client and remote computers are in different domains and there is no trust between the two domains.
After checking for the above issues, try the following:
- Check the Event Viewer for events related to authentication.
- Change the authentication method; add the destination computer to the WinRM TrustedHosts configuration setting or use HTTPS transport. Note that computers in the TrustedHosts list might not be authenticated.
- For more information about WinRM configuration, run the following command: winrm help config.
To refer back to the numbered items in the error message:
- I use a domain admin account to do this.
- Not sure how to change this in Server Manager so I suppose the default should do it.
- I'm running inside the domain, starting Server Manager as a domain admin.
- The server actually has the following SPN's which I haven't touched:
- Dfsr-12F9A27C-BF97-4787-9364-D31B6C55EB04/srv003.rwwilden01.local
- TERMSRV/SRV003
- TERMSRV/srv003.rwwilden01.local
- WSMAN/srv003
- WSMAN/srv003.rwwilden01.local
- RestrictedKrbHost/SRV003
- HOST/SRV003
- RestrictedKrbHost/srv003.rwwilden01.local
- HOST/srv003.rwwilden01.local
- Both computers are in the same domain.
- No events on the client machine.
- It shouldn't be necessary to do this.
-
 MikhailSP about 8 yearsHelped me as well; however the real cause of the issue was related to incorrent SPN records
MikhailSP about 8 yearsHelped me as well; however the real cause of the issue was related to incorrent SPN records -
HTLee about 6 yearsWireshark tip is helpful - it also helps to filter its traffic with "kerberos" to cut down on irrelevant records.
-
Slogmeister Extraordinaire over 4 yearsHow did you do this?
-
Jacob Degeling about 2 yearsThe command to do this is
Reset-ComputerMachinePassword