How to disable autoconfiguration on IPv6 in Linux?
Solution 1
Auto configuration can be disabled temporary for eth1 with:
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.eth1.autoconf=0
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.eth1.accept_ra=0
or for all interfaces with:
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.autoconf=0
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra=0
Reenabling works by using 1 instead of 0 in the call.
Disabling it permanently can be done with an entry to /etc/sysctl.conf.
On Debian Etch (probably on newer too), without setting the accept_ra, the system will autoconfigure using the Link local adress (fe80..)
As Gart mentioned below, automatic address configuration and router discovery will be disabled if the host itself is a router and accept_ra is not 2, i.e
net.ipv6.conf.<iface|all|default>.forwarding=1
and
net.ipv6.conf.<iface|all|default>.accept_ra=0
or net.ipv6.conf.<iface|all|default>.accept_ra=1.
where iface is your interface
Solution 2
The sysctl solution did not work for us on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic.
We solved it by:
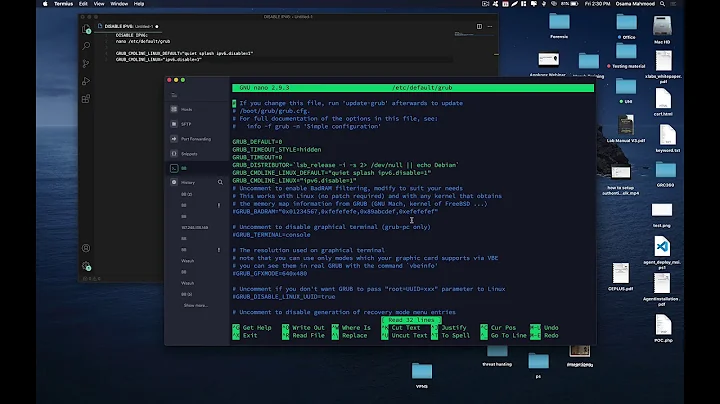
Editing /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml, configure:
network:
...
ethernets:
eth0:
...
dhcp6: no
accept-ra: no
You may need to use your interface name instead of eth0.
After you save the file execute:
netplan apply or reboot
If you already have received an IPv6 IP from autoconfiguration and you want to remove it without rebooting, you can execute:
ip -6 addr del 1111:2222:1:0:aaaa:bbbb:cccc:dddd/64 dev eth0
Of course you need to replace the IP and device in this command.
Solution 3
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra=0 above should not be done, as RAs are necessary for indication of on-link and off-link for the prefix (as per RFC5942), as well as automated configuration of a number of other parameters, such as MTU, Neighbor Discovery timeouts etc.
If you want to disable autoconfiguration, either set the autoconf sysctl off as above, or switch off the A (autoconfiguration bit) in the Prefix Information Option (PIO) in the RA.
Solution 4
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.autoconf=0
This didn't work for me on Debian Wheezy. After examining /etc/sysctl.conf I needed to use
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.autoconf=0
Solution 5
The problem with Ubuntu 18 and ipv6 is that systemd-networkd controls kernel parameters, so though one might disable ipv6 with sysctl, networkd will be more than happy switching them on for you, if the configuration does not state otherwise.
My solution to disable ipv6 is to configure link-local in netplan to an empty scalar (provided you have no link-local ipv4 IPs)
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
eth0:
..
link-local: [ ]
The configuration will compile configuration for networkd that will be posted in /run/systemd/network/10-netplan-eth0.network and that will convince networkd not to put up ipv6 for eth0
If you may want to disable ipv6 also on the loopback, it is easily achieved by setting the kernel parameter net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 to 1. networkd does not seem to control loopback.
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1
Related videos on Youtube
rwadman
Updated on September 17, 2022Comments
-
rwadman over 1 year
How can I permanently disable autoconfiguration of IPv6 in Linux? When I try to manually delete an address from an interface with:
ip -6 addr del 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334/64 dev eth1It will reappear a few seconds later, I want it to be gone permanently, but without disabling IPv6 all together.
-
 Stormy Chase Forrester over 12 yearsAlso, automatic address configuration and router discovery will be disabled if the host itself is a router, i.e
Stormy Chase Forrester over 12 yearsAlso, automatic address configuration and router discovery will be disabled if the host itself is a router, i.enet.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1is set. -
anthonysomerset over 5 yearsthis has just made my day been scratching my head on this for a few months :D
-
Jeroen Vermeulen - MageHost over 5 yearsI usually just scratch Google till I find it.
-
Phil McKerracher over 5 yearsThis worked when I tried it, but the problem is turning accept-ra off is quite dangerous, as mentioned by Mark S - it appears to work but later you may find you're missing packets because they hit a fragmentation point or a failover router is used. Also it breaks pings. The reason I was trying to do this was to reliably match my SPF record in outgoing mail but then I realised I should have been using a netmask in the record instead because in IPv6 a range of addresses effectively belongs to a machine, not a single address.
-
Zoltan about 5 yearsI really like your very clean solution. As we don't use link-local addresses adding the empty scalar the perfect solution. After this, we had to reboot the server as netplan apply kept the already assigned IPv6 addresses on both of our ethernet interfaces. But after reboot, everything works just like you said. I don't think there is a reason to bother with disabling IPv6 on the loopback interface, so I just skipped the sysctl part. Thanks!
-
Marcel Waldvogel over 3 yearsThe kernel only propagates some
net.ipv6.conf.allparameters to all interfaces. Some parameters which need to be present at interface creation time will not be honored here, by design. bugzilla.kernel.org/show_bug.cgi?id=9224 -
Marcel Waldvogel over 3 yearsI am seeing
mngtmpaddras a flag despiteuse_tempaddr=0. And the address is created from the EUI64, so it is definitely not a privacy address. -
Marcel Waldvogel over 3 yearsPlease be careful with disabling router advertisements, so don't use
accept-ra: false! RA is needed for some other network configuration besides the addresses, as @Mark S has explained above: superuser.com/a/635251 -
Thiago Conrado over 3 years@MarcelWaldvogel indeed it is not the best, unfortunately I was unable to achieve the goal with that enabled
-
Marcel Waldvogel over 3 yearsI also gave up. However, the additional SLAAC address did only cause real problems for one application (exposing a UDP port through Docker). I changed the client (in this case Docker) to only listen on the specific additional address.
-
Thiago Conrado over 3 yearsExactly my point, Linux has weak networking, hence you cannot control the outbount IP unless it is a single IP per namespace/vm; in our aplication, as the peer will accept check if the packet came from the define IP in the software level, a second IP just mess up things...
-
Marcel Waldvogel over 3 yearsNormally, applications send UDP replies back from the address the request got in on (using
recvfrom()/sendto()). However, withdocker-proxyas a middleman, the receiving application does not see the original addresses anddocker-proxydoes not know what request the reply is to. In other words: Without Docker, the problem would not show up for servers. -
Marcel Waldvogel over 3 yearsOne thing I haven't tried (because it works for me): Trying to set the preferred lifetime of the SLAAC address to 0 to have it deprecated immediately. freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/…