pacman "exists on filesystem" error
Solution 1
After pacman finally deprecated the --force option and made the surrogate --overwrite option work as expected, the following usage pattern should be noted.
A command to reproduce the --force option that blindly overwrites anything that conflicts is this:
sudo pacman -S --overwrite \* <package_name>
Or
sudo pacman -S --overwrite "*" <package_name>
The tricky part is escaping the wildcard to stop the shell from expanding it first.
Solution 2
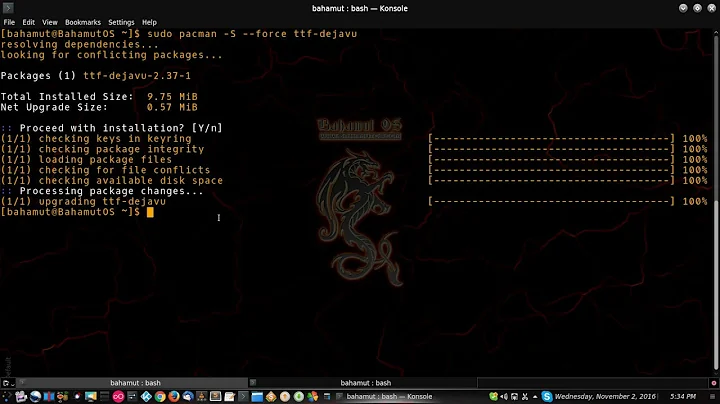
Ok, it looks like running sudo pacman -S --force <package-name> works, but it doesn't resolve conflicting directories. In such cases, running sudo rm -rf on the conflicting directories, followed by sudo pacman -S --force <package-name> works.
Now my pacman -Syu resolves well.
Solution 3
tl;dr: Uninstall the conflicting application before running pacman.
pacman (and other package managers) keep an index of packages and files that they manage (pacman --query --list). Some files, such as configuration, will be marked as modifiable and will not be overwritten during upgrade (except in special circumstances, where the package manager will typically move away the old file before creating the new one). Other files will be marked as unmodifiable. If another application changes those files in any way without updating the index accordingly there's no way for the package manager to know what to do with those files during an upgrade.
Many applications installed using the standard ./configure && make && sudo make install pattern can be uninstalled using sudo make uninstall. If you have installed the application in some other way you might have to something else to uninstall it. In general it can be a good idea to keep a copy of installation files somewhere (for example ~/install) to be able to reliably uninstall them in such cases. Just removing the conflicting files will probably leave other files lying around, which could conceivably cause other problems.
When installing software with other package managers there are ways to isolate those from the system files. This is an established best practice for example during software development, where you really want to keep versions consistent and avoid conflicts with other software. Examples include:
Solution 4
The correct way to upgrade and overwrite conflicting packages is:
sudo pacman --overwrite "*" -Syu
Solution 5
TLDR;
- Get a list of the offending files (copy and paste pacman's output into a file).
- Use awk to strip out everything but the file paths into a new list.
- Use while to move the offending files out of the way, based on the list.
- Run
sudo pacman -Syuagain.
edited to add TLDR and fix typos
Although I'm pretty sure I haven't been doing anything stupid, I've had this problem maybe every other time I've tried to update since I've been using Manjaro; three or four times within two months. Point being, this fixes it.
Get a list of your files.
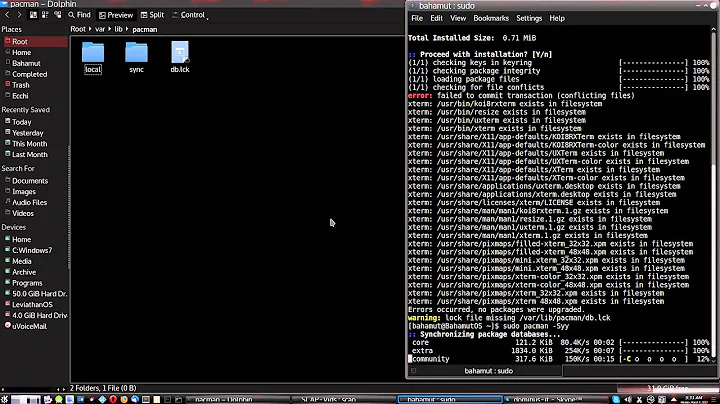
When the update fails in your terminal window, you get this:
error: failed to commit transaction (conflicting files)
evilfile: /usr/bin/evilfile exists in filesystem
libx000: /usr/lib/libx000.so.f.u.loser exists in filesystem
accountsservice: /usr/share/locale/ru/LC_MESSAGES/accounts-service.mo.yu.dnt.evn.spk.russian exists in filesystem
... and a lot more.
Copy the output from the terminal, and put it in a file. I used nano, and named mine "files," as in ~/work/files.
Strip extraneous info:
cat files | awk '{print $2}' >> ~/work/files2
This takes the second "word" from each line and prints it to files2.
Deal with the files
You could delete them, move them, or rename them.
If something breaks, it's easiest to fix if we break it by moving it instead of deleting or renaming it:
mkdir ~/work/oldfiles while read -r file; do sudo mv -- "$file" ~/work/oldfiles/$file; done < files2If you really want to delete them, which there is no reason to do (DANGER DANGER): while read -r file; do sudo rm -- "$file"; done < files2
Updating
To get --overwrite to work, which we need to do to get pacman to realize the package isn't broken, you need the following syntax:
sudo pacman -S package_name --overwrite /location/of/thing- In my case:
sudo pacman -S libidn2 --overwrite /usr/lib/libidn2.so.0 - Following the example:
sudo pacman -S libx000 --overwrite /usr/lib/libx000.so.f.u.loser
- In my case:
I had a cute problem where if I deleted the libidn2.so.0 symlink, nothing worked, and when I put it back, I got the "exists on filesystem" error. The above, with --overwrite, is all that worked for me.
Finally:
sudo pacman -Syu
Related videos on Youtube
modulitos
Updated on September 18, 2022Comments
-
 modulitos 9 months
modulitos 9 monthsI ran
sudo pacman -Syuand I got some interesting errors reading:error: failed to commit transaction (conflicting files)
and a long list of files followed by
exists in filesystem. Full output is here: http://ix.io/lLwIt appears that many of these files are not associated with a package when I checked them with
pacman -Qo <path-to-file>, but I did not check them all. I had a weak connection when I ranpacman -Syu, but I get the same errors when I updated later: http://ix.io/lLxWhat should I do? Should I check all files and delete the ones that do not have an associated package? Should I force update (with
sudo pacman -S --force <package-name>?)Update
I tried running
sudo pacman -S --force <package-name>and got this:[my-pc]/home/average-joe$ pacman -Qo /usr/lib/python3.5/site-packages/PyYAML-3.11-py3.5.egg-info error: No package owns /usr/lib/python3.5/site-packages/PyYAML-3.11-py3.5.egg-infoIt looks like
pacman -S --force <packagedoes not overwrite directories that contain files. From the man:Using --force will not allow overwriting a directory with a file or installing packages with conflicting files and directories.
Should I just delete the conflicting directories? (they do not have associated packages)
-
 Admin over 7 yearswhy do you have conflicting files in the first place? when using a package manager, try not to tap on its toes (e.g. by installing software in places the package manager rightfully thinks is theirs; if you must install things manually, install to
Admin over 7 yearswhy do you have conflicting files in the first place? when using a package manager, try not to tap on its toes (e.g. by installing software in places the package manager rightfully thinks is theirs; if you must install things manually, install to/usr/local/rather than/usr/) -
 Admin over 7 years@umläute I am not exactly sure where the conflicting files came from, but I suspect they are related to my installation of docker-compose which I installed using
Admin over 7 years@umläute I am not exactly sure where the conflicting files came from, but I suspect they are related to my installation of docker-compose which I installed usingsudo pip install -U docker-compose==1.5.0rc3on this page. Perhapssudo pip installconflicts with pacman? -
 Admin about 6 years@umläute Getting wrong
Admin about 6 years@umläute Getting wrong-Supdates (partial installs, etc) will let you that scenario. Case of me--forceworked all times. -
 Admin over 3 yearsSee comment below to "fast" usage of the
Admin over 3 yearsSee comment below to "fast" usage of the--overwritecommand, because--forceis not working anymore. -
 Admin over 2 yearsThis will often happen for CUPS wrappers: Brother printer config files and libraries are packaged in several AUR sources. And
Admin over 2 yearsThis will often happen for CUPS wrappers: Brother printer config files and libraries are packaged in several AUR sources. Andtrizen -S <package> --overwrite "*"or\*won’t work: the*argument isn’t passed on topacman. Not sure how to properly escape this, but after downloading all packages,trizenwill tell you the exactpacmancommand it is going to execute. Then simplyCtrl+C, copy that command, fix the"*"argument and hitEnter.
-
-
 modulitos over 7 yearsSee my comment to @umlaute above. I think the conflict was from a
modulitos over 7 yearsSee my comment to @umlaute above. I think the conflict was from asudo pip installcommand. Perhaps I should avoid using pip with sudo? -
 Ankit Balyan almost 5 years--force is deprecated; use --overwrite instead.
Ankit Balyan almost 5 years--force is deprecated; use --overwrite instead. -
 skhalymon almost 5 years--force is working for me but --overwrite is not
skhalymon almost 5 years--force is working for me but --overwrite is not -
 spydon almost 5 years
spydon almost 5 yearssudo pacman -Syu --forceworked for me, but overwrite wasn't recognized. -
 xsilen T over 3 years--overwrite seems must specify what to overwrite. currently use --force every thing is fine
xsilen T over 3 years--overwrite seems must specify what to overwrite. currently use --force every thing is fine -
 m3nda over 3 yearsThis time nothing worked for me, caused by dependancy loop, I had no more choice than uninstall the module with pip then issue again the pacman install one. So sad :-/ that creators or those packages don't look at those problems.
m3nda over 3 yearsThis time nothing worked for me, caused by dependancy loop, I had no more choice than uninstall the module with pip then issue again the pacman install one. So sad :-/ that creators or those packages don't look at those problems. -
 Labo over 2 yearsno syntax works with
Labo over 2 yearsno syntax works with--force, this answer should be edited to refer to the other one -
 Volker Weißmann over 2 yearsThis is out of date. You need to use --overwrite instead of --force.
Volker Weißmann over 2 yearsThis is out of date. You need to use --overwrite instead of --force. -
 Kusalananda over 2 years@Kryptomatrix Could you possibly suggest an update to this answer?
Kusalananda over 2 years@Kryptomatrix Could you possibly suggest an update to this answer? -
 Volker Weißmann over 2 years@Kusalananda This one is correct unix.stackexchange.com/a/549419/434628
Volker Weißmann over 2 years@Kusalananda This one is correct unix.stackexchange.com/a/549419/434628 -
 Kusalananda over 2 years@Kryptomatrix Whether one or the other is "correct" appears to depend on the version of
Kusalananda over 2 years@Kryptomatrix Whether one or the other is "correct" appears to depend on the version ofpacmanbeing used. -
 Volker Weißmann over 2 yearsYes, and for the newest verision of pacman the correct answer is --overwrite.
Volker Weißmann over 2 yearsYes, and for the newest verision of pacman the correct answer is --overwrite. -
 Hi-Angel about 1 yearDoesn't work. It still prints an error about existing file in the filesystem. However, suggested idea below about simply removing the conflicting files and then installing as usual worked for me.
Hi-Angel about 1 yearDoesn't work. It still prints an error about existing file in the filesystem. However, suggested idea below about simply removing the conflicting files and then installing as usual worked for me. -
 Admin about 1 yearIt worked for me. In my case I had faced a package issue like
Admin about 1 yearIt worked for me. In my case I had faced a package issue likeedk2-armvirt already exists in filesystem.