qemu process memory usage greater than guest memory usage
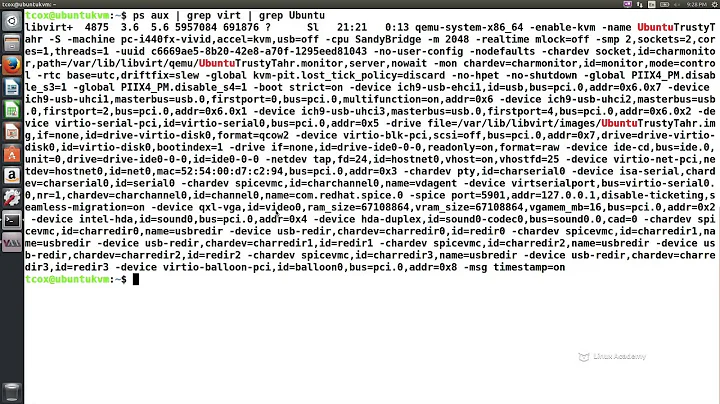
What I'm trying to understand is how come Guest 1 currently uses 2.5G but corresponding qemu processes uses 9.6G physical RAM on the host.
According the data you posted higher up, your guest 1 is using 13G of the memory allocated to it by the host (split between allocations for processes & allocations for cache). Your host only shows 9.6 G resident so some of that 13GB has been pushed out to swap I presume.
Related videos on Youtube
Jérôme
Updated on September 18, 2022Comments
-
Jérôme almost 2 years
I have a physical machine with 24 GB RAM hosting a few VMs using libvirt-qemu.
When creating VMs, I assign a lot of memory and no swap, so that the total of assigned memory can be greater than the physical memory on the host, and the swap is managed globally at host level. I found this advice on the Internet and it makes sense to me.
I recently found out we have memory issues and before adding physical memory to the machine, I launched
htopin the host and the guests, and there's something I don't quite understand.Guests
Guest 1
- Total: 16G
- Used: 2.5G
- Used + Cache: 13G
Guest 2
- Total: 16G
- Used: 1.8G
- Used + Cache: 3.6G
Guest 3
- Total: 10G
- Used: 0.5G
- Used + Cache: 1G
... (ignoring a few smaller guests)
Host
- Total: 23.5G
- Used: 23.2G
- Used + Cache: 23.5G
- Swap total: 18.6G
- Used: 12.5G
List of processes on host (I only copied guest 1, 2 and 3 in numerical order):
PID USER PRI NI VIRT RES SHR S CPU% MEM% TIME+ Command 2212 libvirt-q 20 0 21.3G 9.6G 3476 S 118. 41.0 1867h qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -name guest=guest_1 ... 2391 libvirt-q 20 0 21.2G 2455M 1020 S 4.0 10.2 56h49:10 qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -name guest=guest_2 ... 40694 libvirt-q 20 0 14.7G 7545M 1668 S 1.3 31.4 94h35:35 qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -name guest=guest_3 ... ...What I'm trying to understand is how come Guest 1 currently uses 2.5G but corresponding qemu processes uses 9.6G physical RAM on the host.
All machines are Debian, if that matters. Host is debian Stratch and guests are Stretch and Jessie.
-
Jérôme over 5 yearsYou're right. I overlooked the cache issue. I guess the RAM over-allocation policy I use when creating the VMs is flawed as the host only sees memory usage without used/cache discrimination.
-
Jérôme over 5 yearsYet, I don't get why guest_3 uses 7545M (7.5G) from the host while its total use (cache included) is around 1G.
-
DanielB over 5 yearsWhen QEMU gives a guest 10 GB of RAM, this is not allocated from the host immediately in a default configuration, it is merely mapped into the address space, so host side resident RAM is initially quite small. As the guest OS touches memory pages, they get faulted in on the host and QEMU's resident memory allocation thus grows. This is a one-way process though - when the guest OS stops using a memory page, nothing will "un-fault" the memory page in the host. IOW, QEMU is using 7.5 GB for guest 3, because at some point in the past the guest OS has really used 7.5 GB.
-
Jérôme over 5 yearsOK, so over-allocating makes even less sense. I thought the point was that VMs might have their memory consumption peaks at different moments in time, so the host would only swap when, bad luck, many VMs need much RAM at the same time, otherwise a VM peak would be compensated by other VMs needing fewer RAM. But if the host does not get the RAM back after a peak, the whole strategy is broken, right?
-
Jérôme over 5 yearsThis is even more broken because what the guests use is not exactly what they need, but rather what they can get, as they can be greedy for cache while they don't actually need that much RAM, so providing them a high memory cap makes them ask for more memory the host will never get back.
-
DanielB over 5 yearsThe host will get the RAM back after a peak in so much as it is free to push that pages of RAM out to swap when untouched. The host cannot simply discard the pages because it does not know that they are not used - the guest might have data in them. All the host can tell is that a page hasn't been accessed for N length of time.
-
DanielB over 5 yearsIf overcommitting you must have sufficient RAM+swap space combined for the worst case usage pattern. Bear in mind QEMU uses RAM beyond that which is allocated for the guest memory. eg for VNC/SPICE framebuffers, for BIOS regions, for general I/O handling and more. So you should account for at least another 300-500 MB per guest on top to be safe against OOM. If swapping is not acceptable for your performance requirements then it is advisable to not overcommit RAM at all.
-
Jérôme over 5 yearsThanks. Things are much clearer to me now and I learnt a lot about memory management. I did have an issue as I had allocated more in total than host RAM + swap and I just fixed that. So when overcommitting, if a guest uses a lot of frequently accessed cache memory, the host won't send that to swap, and another guest might have its actually used (i.e. not cache) RAM swapped in host. Not sure I'm clear, I mean I find it surprising there does'nt seem to be a way to ensure that all guests used (+- necessary) RAM have priority over all guests cache (+- bonus) RAM when it comes to host RAM vs. swap.
-
DanielB over 5 yearsFundamentally the problem you're facing is that the guest RAM usage is a blackbox from the host OS pov. There have been proposals to define mechanisms for cooperation between guests & hosts wrt to page cache in particular, but nothing has really come to fruition.
![How To Fix High RAM/Memory Usage on Windows 10 [Complete Guide]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/osKnDbHibig/hq720.jpg?sqp=-oaymwEcCNAFEJQDSFXyq4qpAw4IARUAAIhCGAFwAcABBg==&rs=AOn4CLDgajRq6bP7JD1erNguFVloL0gqUA)