What characters have to be escaped to prevent (My)SQL injections?
Solution 1
The MySQL manual page for strings says:
-
\0An ASCII NUL (0x00) character. -
\'A single quote (“'”) character. -
\"A double quote (“"”) character. -
\bA backspace character. -
\nA newline (linefeed) character. -
\rA carriage return character. -
\tA tab character. -
\ZASCII 26 (Control-Z). See note following the table. -
\\A backslash (“\”) character. -
\%A “%” character. See note following the table. -
\_A “_” character. See note following the table.
Solution 2
A guess concerning the backspace character: Imagine I send you an email "Hi, here's the query to update your DB as you wanted" and an attached textfile with
INSERT INTO students VALUES ("Bobby Tables",12,"abc",3.6);
You cat the file, see it's okay, and just pipe the file to MySQL. What you didn't know, however, was that I put
DROP TABLE students;\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b\b
before the INSERT STATEMENT which you didn't see because on console output the backspaces overwrote it. Bamm!
Just a guess, though.
Edit (couldn't resist):
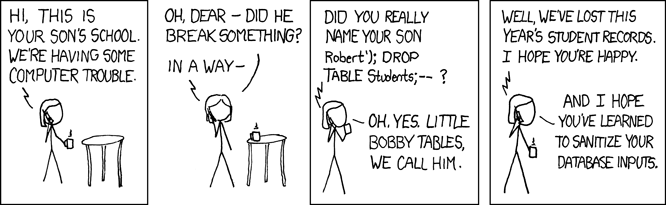
Solution 3
Blacklisting (identifying bad characters) is never the way to go, if you have any other options.
You need to use a conbination of whitelisting, and more importantly, bound-parameter approaches.
Whilst this particular answer has a PHP focus, it still helps plenty and will help explain that just running a string through a char filter doesn't work in many cases. Please, please see Do htmlspecialchars and mysql_real_escape_string keep my PHP code safe from injection?
Tower
Updated on September 09, 2020Comments
-
Tower almost 4 years
I'm using MySQL API's function
mysql_real_escape_string()Based on the documentation, it escapes the following characters:
\0 \n \r \ ' " \ZNow, I looked into OWASP.org's ESAPI security library and in the Python port it had the following code (http://code.google.com/p/owasp-esapi-python/source/browse/esapi/codecs/mysql.py):
""" Encodes a character for MySQL. """ lookup = { 0x00 : "\\0", 0x08 : "\\b", 0x09 : "\\t", 0x0a : "\\n", 0x0d : "\\r", 0x1a : "\\Z", 0x22 : '\\"', 0x25 : "\\%", 0x27 : "\\'", 0x5c : "\\\\", 0x5f : "\\_", }Now, I'm wondering whether all those characters are really needed to be escaped. I understand why % and _ are there, they are meta characters in LIKE operator, but I can't simply understand why did they add backspace and tabulator characters (\b \t)? Is there a security issue if you do a query:
SELECT a FROM b WHERE c = '...user input ...';Where user input contains tabulators or backspace characters?
My question is here: Why did they include \b \t in the ESAPI security library? Are there any situations where you might need to escape those characters?
-
 balpha almost 15 yearsThanks Stefano, that fulfills the attribution clause of the CC license.
balpha almost 15 yearsThanks Stefano, that fulfills the attribution clause of the CC license. -
mR_fr0g about 10 yearsLink it dead. Consider updating.
-
 Bing over 6 yearsIf you're trying to store a name, like O'Leary, you would mess up the person's name. If you're storing a sentence like
Bing over 6 yearsIf you're trying to store a name, like O'Leary, you would mess up the person's name. If you're storing a sentence like"Help!", David yelled.you'd want to keep the double-quotes. So yeah, in some cases dumping special characters might be fine, but not in all. -
The Godfather almost 5 yearsThis doesn't answer the part of the question where it asks "why?"
-
 Brian Leishman almost 5 yearsKeep in mind you probably don't want to always escape
Brian Leishman almost 5 yearsKeep in mind you probably don't want to always escape%and_since the back slash will get passed literally unless used in a filter/search context, e.g.\%will look like the string\%when using=and%when usinglike